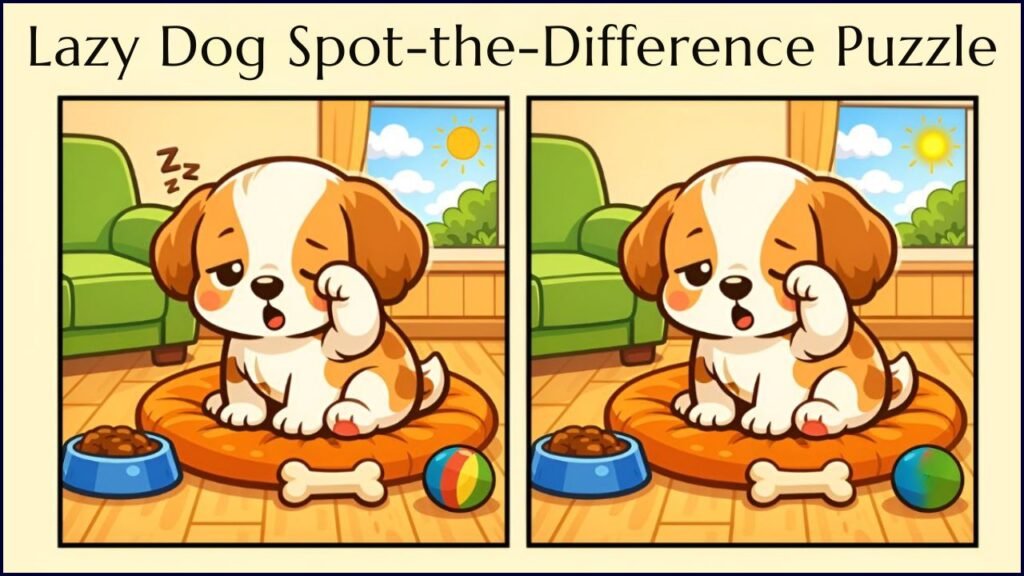
The Lazy Dog Spot-the-Difference Puzzle, a deceptively simple visual challenge circulating widely on social media and news aggregation platforms, has drawn global attention for how consistently it misleads viewers. The puzzle presents two nearly identical illustrations of a sleeping dog and asks users to identify subtle differences within seconds, revealing fundamental limits in human attention, perception, and confidence.
Table of Contents
Lazy Dog Spot-the-Difference Puzzle
| Key Fact | Detail |
|---|---|
| Number of differences | Three confirmed visual changes |
| Core cognitive effect | Change blindness |
| Average solve time | Over 20 seconds without hints |
| Platform spread | Facebook, X, Instagram, news sites |
| Why it works | Familiar scene reduces scrutiny |
A Viral Puzzle With Unusual Staying Power
The Lazy Dog Spot-the-Difference Puzzle first appeared on niche puzzle and riddle websites before spreading rapidly across mainstream social platforms. Within weeks, screenshots of the image were being shared millions of times, often accompanied by captions challenging friends to “find all three differences in 10 seconds.”
Unlike many viral brain teasers that depend on shock value or exaggerated optical illusions, this puzzle’s strength lies in restraint. The illustration is calm, domestic, and visually comforting. A dog sleeps peacefully in a tidy room, toys resting nearby, sunlight entering through a window.
That calmness lowers defenses.
“The puzzle feels non-threatening,” said Dr. Rebecca Lawson, a cognitive psychologist at the University of Liverpool who studies visual processing. “People approach it casually, which is precisely when attention errors are most likely to occur.”
Unlike novelty-based viral content that fades quickly, the Lazy Dog Spot-the-Difference Puzzle has maintained engagement over time. Media analysts attribute this longevity to its repeatability. Viewers frequently return to the image after failing the first attempt, often convinced they missed something obvious.
What Makes the Puzzle Difficult
At the heart of the challenge is change blindness, a phenomenon in which observers fail to notice changes in a visual scene, particularly when those changes are subtle or occur in familiar contexts.
Decades of research show that human vision does not function like a camera. Instead, the brain constructs a simplified representation of the world, prioritizing meaning over detail.
“People assume visual perception is continuous and complete,” said Dr. Stephen Mitroff, a professor of psychology at George Washington University. “In reality, attention is selective. When scenes are stable and predictable, the brain actively filters out information it considers non-essential.”
The Lazy Dog Spot-the-Difference Puzzle exploits this filtering mechanism. Because the scene feels ordinary, viewers rely on expectation rather than inspection. Their brains register “sleeping dog” and “cozy room” and stop scanning aggressively.
This effect is compounded by symmetry. The two images are nearly identical in composition, color balance, and spacing. Without obvious anchors for comparison, the visual system struggles to detect discrepancies.
The Confirmed Differences
After widespread speculation and user debate, puzzle creators eventually released official solutions confirming three intentional differences:
- Sun rays in the window: One image includes an extra ray extending from the sun, subtly altering the light pattern.
- Color of the toy ball: The ball near the dog shifts from a solid color in one image to a multicolored pattern in the other.
- Sleep indicator symbols: One “Z” above the dog’s head is missing in the altered image.
Individually, each change is minor. Together, they create a scenario where viewers often notice one or two differences but miss the third entirely.
This partial success is psychologically important. Studies show that finding some differences increases confidence, reducing the likelihood that viewers will continue searching thoroughly.
Why Time Pressure Matters
Many versions of the Lazy Dog Spot-the-Difference Puzzle emphasize speed, challenging users to solve it in under 10 seconds. That instruction dramatically affects outcomes.
“When people are rushed, they prioritize overall meaning rather than precise detail,” said Dr. Lawson. “Time pressure pushes the brain into efficiency mode.”
In efficiency mode, the brain scans for anomalies that disrupt the scene’s logic. Because none of the differences alter the story of the image—the dog remains asleep, the room remains intact—those anomalies go undetected.
This mirrors real-world behavior. Drivers often miss unexpected objects on familiar roads, and professionals reviewing documents can overlook errors they have seen many times before.
The Role of Confidence and Social Sharing
One reason the puzzle spreads so effectively is emotional response. Users often feel certain they have identified all differences, only to discover they are wrong.
That gap between confidence and accuracy drives sharing.
“People post these puzzles not just to challenge others, but to validate themselves,” said Marcus Chen, a digital culture researcher at the University of Southern California. “When they fail, they want to see who else fails too.”
Social platforms amplify this effect by rewarding engagement. Comments debating possible differences often outnumber correct answers, extending the puzzle’s lifespan in algorithms that prioritize discussion.
A Broader Trend in Visual Perception Tests
The Lazy Dog Spot-the-Difference Puzzle belongs to a wider category of viral visual challenges that surged during recent years. These include hidden-object images, ambiguous figures, and rapid comparison tests.
The appeal is partly practical. Such puzzles require no specialized knowledge, cross language barriers, and work equally well on mobile devices. They also provide a sense of productivity without obligation.
During periods of heightened screen use, including pandemic lockdowns, engagement with visual puzzles increased sharply, according to platform analytics.
Psychologists caution against overstating cognitive benefits. While puzzles can improve task-specific skills, there is limited evidence they produce lasting improvements in intelligence or memory.
However, experts agree they serve an educational role by revealing how perception works.
Educational and Professional Implications
Beyond entertainment, change blindness has implications in fields where visual accuracy is critical.
Medical imaging specialists, air traffic controllers, and quality inspectors all face environments where small visual differences matter. Training programs in these professions increasingly include awareness exercises designed to counteract attentional blindness.
“The lesson from puzzles like this is humility,” said Dr. Mitroff. “Even trained observers miss things. Systems should be designed to account for that.”
Some educators have incorporated spot-the-difference puzzles into classrooms as teaching tools for attention and scientific reasoning, encouraging students to question assumptions and slow down observation.
Why Familiar Scenes Are the Most Dangerous
One of the most striking aspects of the Lazy Dog Spot-the-Difference Puzzle is its setting. Research shows people are more likely to miss changes in familiar environments than in unfamiliar ones.
The brain assumes stability in known contexts. That assumption reduces cognitive load but increases vulnerability to error.
In contrast, unusual or chaotic scenes trigger heightened vigilance. Ironically, the more relaxed the image, the more deceptive it becomes.
What Comes Next
Puzzle designers continue refining these challenges, making differences smaller and scenes more realistic. Some now use artificial intelligence to generate images calibrated to exploit known perceptual biases.
As audiences grow more aware of these effects, puzzles may evolve to remain effective. However, experts say the underlying limitations of attention are unlikely to disappear.
“Human perception hasn’t changed,” said Dr. Lawson. “We are still operating with the same cognitive shortcuts. That’s why these puzzles keep working.”
FAQ
How many differences are in the Lazy Dog Spot-the-Difference Puzzle?
There are three confirmed differences between the two images.
Is the puzzle timed?
Many versions suggest a 10-second limit, though accuracy improves without time pressure.
What cognitive skill does the puzzle test?
The puzzle primarily tests visual attention and susceptibility to change blindness.
Why do people miss obvious details?
Because the brain prioritizes meaning and familiarity over detailed inspection.

















